
The quest to find the best forex trading strategy is both a science and an art, weaving together technical knowledge, market psychology, and personal discipline. Forex trading, with its vast liquidity and 24-hour nature, offers myriad approaches for traders to capitalize on currency movements. Yet, selecting the most effective strategy demands a careful balance of market conditions, risk tolerance, and trading objectives.
As trader and author Kathy Lien once said, “A trading strategy is a formula for survival and success — not just a path to profit.”
Best Forex Trading Strategy: Comparison Table of the Best 5 Strategies
| Strategy | Timeframe | Market Type | Key Tools | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Trend Following | Medium to Long | Trending Markets | Moving Averages, MACD, RSI | Captures large moves, clear signals | Can produce false signals in choppy markets |
Range Trading | Short to Medium | Sideways/Range-Bound | Support & Resistance, Stochastics | Good for stable markets, less risky | Fails in strong trends |
Breakout Trading | Short to Medium | Volatile, Breakout | Bollinger Bands, Volume | Early entry into new trends | Risk of false breakouts |
Carry Trade | Long | Stable Interest Rate Differentials | Economic Calendars, Interest Rates | Generates steady income from interest | Exposure to currency risk and sudden moves |
Scalping | Very Short | Highly Liquid Markets | Tick Charts, Level 2 Data | Quick profits, high win rate | Requires fast execution, high transaction costs |
Understanding the Landscape of Forex Trading Strategies
Before diving into specific approaches, it is crucial to grasp what makes a forex trading strategy effective. At its core, a strategy should provide clear rules for entry and exit, risk management, and adaptability to changing market dynamics. Not all strategies fit all traders or markets — some excel in trending environments, others in range-bound conditions.
What Is the Best Forex Trading Strategy?
This question does not admit a one-size-fits-all answer. Instead, the best strategy aligns with individual preferences, experience, and goals. For example, an intraday trader may favor forex day trading strategies that capture short-term price movements, whereas a longer-term trader might prefer swing or position trading strategies that ride bigger trends over days or weeks.
Industry expert Boris Schlossberg, co-founder of BK Forex, states,
“The best forex strategy is the one you can follow consistently and with discipline.”
This underscores that the human element—psychological resilience and execution—is as vital as the strategy itself.
Five Effective Forex Trading Strategies to Consider
Exploring different approaches can help illuminate what may work best. Here are five strategies widely regarded as effective:
1. Trend Following Strategy
Trend following is one of the most classic and widely used forex strategies. It involves identifying a strong market direction—uptrend or downtrend—and entering trades that align with that momentum. Traders typically rely on technical indicators such as moving averages (e.g., 50-day and 200-day), the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), or the Relative Strength Index (RSI) to confirm trends.

Why it works: Markets often exhibit prolonged trends, and riding these can lead to significant profits. The famous saying “The trend is your friend” encapsulates this idea. However, trend following can generate false signals in choppy or sideways markets, which require disciplined stop-loss placement to manage risks.
Best used in: Trending markets with clear directional movement.
2. Range Trading Strategy
Range trading exploits periods when the price oscillates between defined support and resistance levels without trending strongly in either direction. Traders buy near support levels and sell near resistance, often confirmed by oscillators like Stochastic or RSI indicating overbought or oversold conditions.
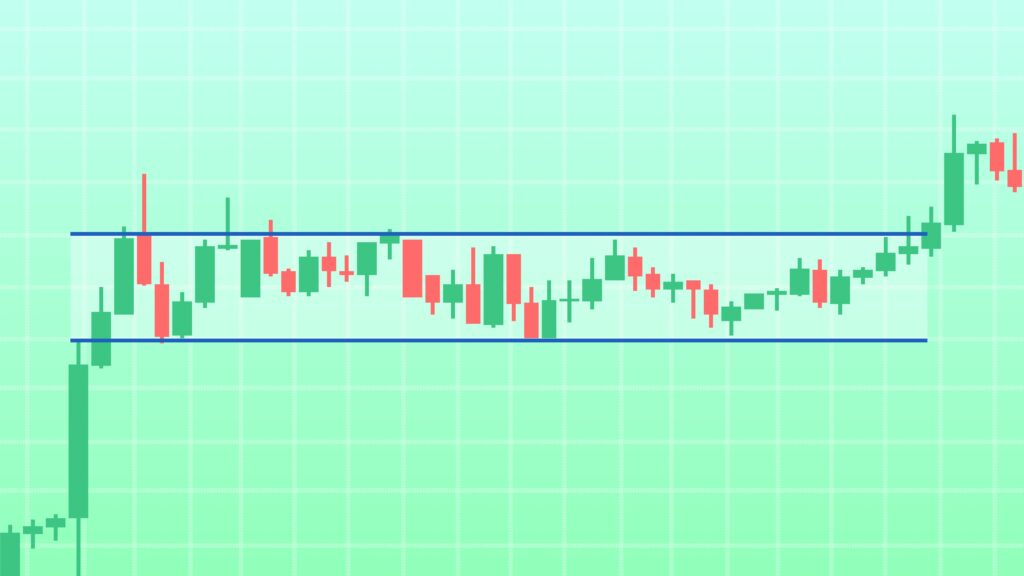
Why it works: Forex pairs often move sideways for extended periods, especially during low volatility or between major economic events. Range trading allows traders to capture predictable reversals in these conditions.
Risks: The strategy can fail during breakouts when price exits the established range abruptly, leading to losses if stops are not placed properly.
Best used in: Sideways or consolidating markets with clear horizontal boundaries.
3. Breakout Strategy
Breakout trading aims to capitalize on significant price moves that occur when the market breaks through established support or resistance levels. Traders often combine volume indicators and volatility measures, such as Bollinger Bands, to confirm the strength of a breakout.
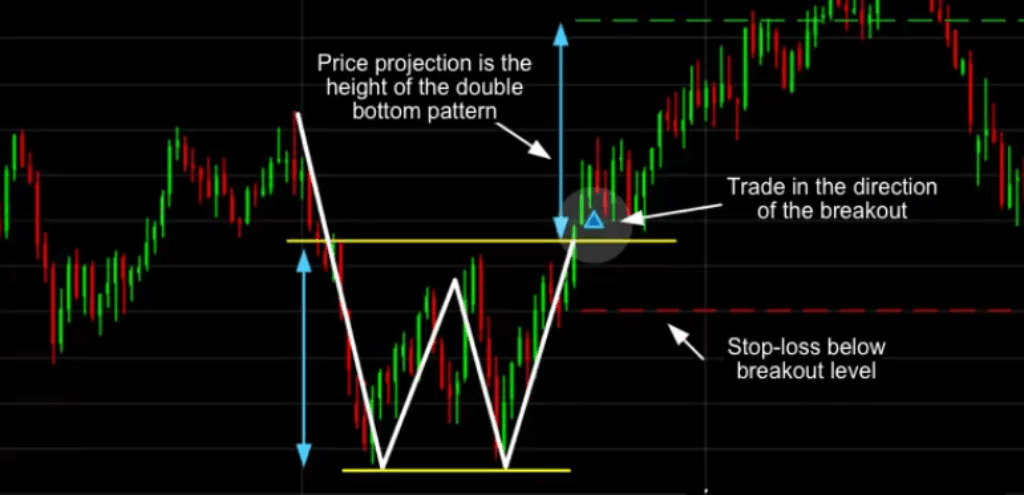
Why it works: Breakouts often signal the beginning of a new trend or a significant shift in market sentiment, offering the chance to enter early for substantial gains.
Challenges: False breakouts are common, where price briefly crosses a level but reverses sharply. Effective risk management with tight stop losses is essential.
Best used in: Periods following consolidation or chart patterns like triangles, flags, or rectangles.
4. Carry Trade Strategy
Carry trading leverages differences in interest rates between two currencies. Traders buy currencies with higher interest rates and sell those with lower rates, aiming to earn the interest rate differential (the “carry”) in addition to any price appreciation.
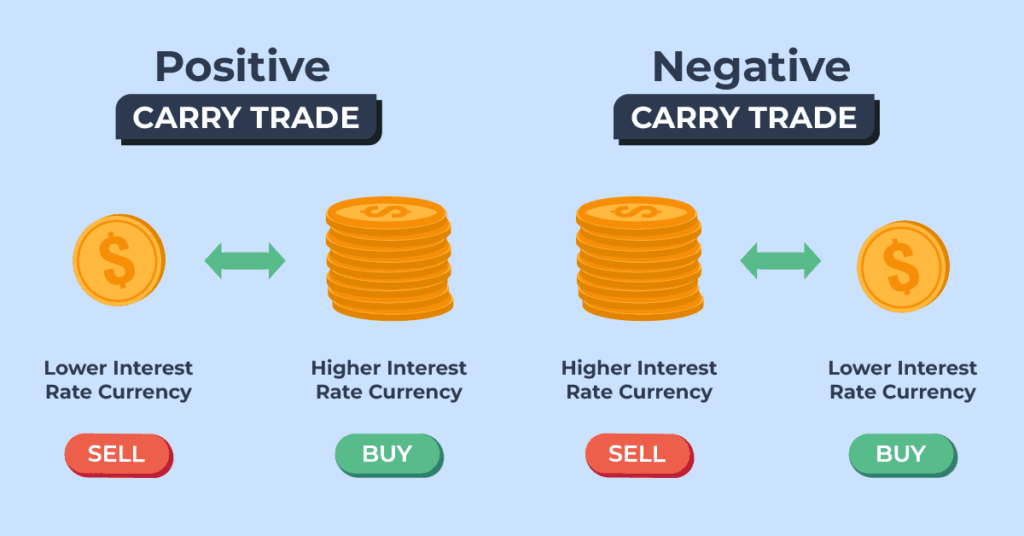
Why it works: The carry trade can generate steady returns when markets are stable, and interest rate spreads are wide.
Risks: Sudden currency devaluations or shifts in global risk appetite can cause large losses, as carry trades often unwind quickly during market turmoil.
Best used in: Low-volatility environments with stable macroeconomic conditions and predictable central bank policies.
5. Scalping Strategy
Scalping is a high-frequency trading approach focusing on making small profits from numerous trades throughout the day. Scalpers use very short timeframes (seconds to minutes) and rely on order flow data, Level 2 quotes, and tick charts.
Why it works: By targeting small price movements repeatedly, scalpers can accumulate significant gains while minimizing exposure to market risks.
Requirements: Scalping demands excellent execution speed, low spreads, and strong discipline, as losses from a single trade can negate many small wins.
Best used in: Highly liquid, low-spread currency pairs like EUR/USD during active trading hours.
Each strategy has nuances and variants, with some traders combining multiple methods depending on market context.
Learning Forex Trading Step by Step
The journey to mastering the best forex strategy ever starts with education and practice:
- Start with Fundamentals: Understanding currency pairs, economic indicators, and how geopolitical events affect forex markets builds a solid foundation.
- Develop a Trading Plan: This includes defining risk tolerance, capital allocation, and preferred trading style.
- Backtesting: Testing strategies against historical data helps identify strengths and weaknesses.
- Demo Trading: Practicing in simulated environments refines execution without risking capital.
- Continuous Learning: Markets evolve, and so should strategies.
It is important to remember that no strategy guarantees profits. According to Dr. Alexander Elder, a well-known trader and author, “The best strategy is worthless without risk management.”
Characteristics of the Most Profitable Trading Strategy
Identifying what makes a trading strategy truly profitable requires more than just spotting quick wins or chasing trends. The most successful forex strategies share a set of fundamental characteristics that support consistent, sustainable gains while protecting capital from unpredictable market movements.
1. Clear Entry and Exit Rules
At the heart of any profitable strategy lies unambiguous rules for entering and exiting trades. Vague or subjective criteria lead to hesitation and inconsistent decisions, which can erode profits. These rules often rely on technical indicators, price action signals, or fundamental triggers that signal high-probability opportunities.
For instance, a strategy might specify entering a trade when the 50-day moving average crosses above the 200-day moving average (a classic “golden cross”) and exiting when momentum wanes or a stop loss is hit. Clarity in these conditions removes guesswork, allowing traders to act swiftly and confidently.
2. Robust Risk Management
Perhaps the single most important trait is a rigorous approach to risk management. Even the best strategies can encounter losing streaks, so controlling potential losses is essential for survival and long-term profitability.
Effective risk management includes setting stop-loss orders to limit downside exposure, sizing positions appropriately relative to the trading account, and avoiding over-leveraging. Typically, risking no more than 1-2% of total capital on any single trade is recommended. This approach ensures that no single loss can significantly damage the account, enabling traders to stay in the game and capitalize on winning trades over time.
3. Adaptability to Market Conditions
Markets are dynamic and can shift from trending to ranging environments quickly. A profitable strategy must either adapt to these changing conditions or be flexible enough to be complemented with other approaches.
For example, a pure trend-following system may struggle during sideways markets, leading to multiple false signals. In contrast, a strategy that incorporates filters or switches between trend and range modes can navigate different phases more effectively.
As trading legend Paul Tudor Jones says, “The most important rule is to play great defense, not offense.” Adaptability helps defend profits in volatile or uncertain markets.
4. Simplicity and Practicality
Complexity does not guarantee success. In fact, overly complicated strategies often fail because they are difficult to execute reliably or lead to “paralysis by analysis.” The most profitable systems balance sophistication with simplicity, using a manageable number of indicators or rules that align with the trader’s cognitive style.
Simplicity enhances execution speed, reduces errors, and builds confidence, which is crucial for maintaining discipline during stressful periods.
5. Consistency and Discipline
A profitable strategy demands consistent application and discipline. Deviations from the plan, driven by emotions such as fear or greed, often result in poor outcomes despite sound strategy design.
Consistency means following the rules even during losing streaks or when tempted to deviate due to impatience. The discipline to stick with tested setups and risk parameters separates successful traders from amateurs.
6. Positive Risk-Reward Ratio
A well-constructed strategy offers a favorable risk-reward profile, meaning potential profits outweigh potential losses. For example, targeting a reward twice as large as the risk taken (a 2:1 ratio) allows traders to be profitable even if only half their trades win.
Balancing risk-reward ratios helps optimize profitability over many trades rather than focusing solely on win rate percentages.
Essential Components of a Profitable Forex Trading Strategy
| Component | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Clear Entry & Exit Rules | Specific signals and conditions for trades | Ensures consistency and reduces hesitation |
| Risk Management | Position sizing, stop losses, risk limits | Protects capital and manages drawdowns |
| Market Adaptability | Ability to adjust strategy in different market phases | Improves long-term success across regimes |
| Simplicity | Easy-to-follow rules without unnecessary complexity | Enhances execution and psychological comfort |
| Consistency & Discipline | Following the plan faithfully | Prevents emotional trading mistakes |
| Positive Risk-Reward | Targeting profits larger than potential losses | Maximizes profitability over time |
Practical Tips for Choosing a Forex Trading Strategy
- Match Strategy to Personality: An aggressive trader may suit scalping, while a patient trader may prefer swing trading.
- Consider Market Conditions: Trend-following may fail in choppy markets; range trading is better suited.
- Evaluate Time Commitment: Day trading demands constant monitoring; position trading allows a more relaxed pace.
- Assess Costs: Frequent trading incurs higher spreads and commissions.
- Test and Refine: Start small, analyze performance, and tweak accordingly.
Conclusion
Selecting the best forex trading strategy is a nuanced decision that intertwines market knowledge, personal temperament, and disciplined execution. There is no definitive “best” strategy universally; instead, effectiveness depends on alignment with individual goals and market conditions. Traders who focus on robust risk management, clear rules, and continuous adaptation stand the best chance of sustained success. As has been discussed earlier in the article, the journey is iterative—consistent evaluation and refinement of strategies pave the way for long-term profitability in the dynamic world of forex.
FAQs
What is the best forex trading strategy for beginners?
For beginners, a simple trend-following strategy or range trading with clear rules is often advisable. These strategies are easier to learn, require less frequent trading, and help build foundational skills without excessive risk.
How can risk management be incorporated into a forex strategy?
Risk management involves setting stop losses, limiting exposure to a small percentage of capital per trade (typically 1–2%), and using proper position sizing. It protects traders from large losses and helps preserve capital for future opportunities.
Are automated forex trading strategies effective?
Automated strategies, or expert advisors (EAs), can execute trades without emotion and follow predefined rules precisely. However, they require careful testing and monitoring, as market conditions may change, reducing their effectiveness.
How important is psychological discipline in forex trading?
Psychological discipline is paramount. Even the most profitable strategy can fail if traders act impulsively or deviate from their plan. Maintaining emotional control and patience is essential for consistent results.

















